Office 文件解析入门
概述 - Office 解析相关协议
这里所讲的 Office 文件指的是微软 Office2007 及以后的 PPT/EXCEL/WORD 等文件格式,因为 Office2007 以前的文件是用二进制格式定义的,不在本文的讨论内容中。
Office2007 以后的文件格式属于 OOXML 文件格式,OOXML 是基于 zip+xml 定义的。
OOXML 全称 Office Open XML File Formats,最初是由 ECMA-376 定义的,它目前已经到第六版。后来 ISO/IEC 29500 也开始掺和OOXML格式的定义,不过可以认为从 ECMA-376 的第2版开始,这两个标准是一样的。目前最新的 OOXML 标准是在 2016 年发布的 ECMA-376 5th edition 或者 ISO/IEC 29500:2016。
微软的 Office 实现了OOXML格式,但不是全部,微软在 这篇文章 中描述了其对标准的支持情况。
OOXML = OPC + *ML ,下面会分别介绍 OPC 和 *ML。
由于 EMCA 文档可以免费在网上下载的,而 ISO 文档需要付费才能获取,因此下文的内容都是基于 ECMA-376 文档。
OPC - Open Package Convention
关于 OPC 的详细内容请参考
ECMA-376,Fourth Edition,Part 2。
OPC 中文名开放打包协定,是一种基于 zip+xml 定义的文件存储格式。一个 OPC 文件(不管其文件后缀是什么)本质上就是一个 zip 文件,你可以用任何常见的解压软件进行解压,解压后你看到的那些文件的组织结构,就是以 OPC 定义的方式存储的。下图是一个PPTX文件解压后的目录结构:
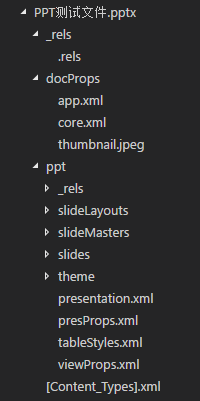
OPC 中有3个重要的概念要理解:Part , Relationship , ContentTypes。
Part
Part 可以简单理解为 zip 中的文件,每一个文件都是一个 Part ,它可以是任何格式,比如图片,xml文件等。在 Office 文件中,各种 Markup Language 定义的内容就作为 XML 存储在 Part 中。
Relationship
Relationship 是一种特殊的 Part ,它描述了各 Part 之间的依赖关系。根据OPC协议的规定,所有的 Relationship 都必须存储在名为 _rels 的文件夹中,并且所有 Relationship 的文件名都必须以 .rels 为后缀。
每一个 Part 根据业务需求都可以有对应的 Relationship 文件,比如在 PPTX 文件中,有一个 Part 为 /ppt/presentation.xml ,它对应的 Relationship 文件(只能)为/ppt/_rels/presentation.xml.rels ,不能是任何其它名字或者位置的文件。下面是一个 PPTX 文件中的 presentation.xml.rels 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<Relationships xmlns="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/package/2006/relationships">
<Relationship Id="rId3" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/slide" Target="slides/slide2.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId7" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/tableStyles" Target="tableStyles.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId2" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/slide" Target="slides/slide1.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId1" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/slideMaster" Target="slideMasters/slideMaster1.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId6" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/theme" Target="theme/theme1.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId5" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/viewProps" Target="viewProps.xml"/>
<Relationship Id="rId4" Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/presProps" Target="presProps.xml"/>
</Relationships>
Relationship 文件的根节点是 RelationShips, 它是 Relationship 节点的集合,每一个 Relationship 节点都代表一个依赖关系。它的各个属性的意义如下:
| 属性名 | 是否必须 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
Id |
是 | 唯一标识符,在当前文件中是唯一的,不同文件中可以重复 |
Type |
是 | Target 的文件类型 |
Target |
是 | 目标 Part 的路径,可以用相对路径也可以用绝对路径 |
TargetMode |
否 | 目标的类型,值可以是 Internal 或者 External (默认是Internal),表示 Target 是OPC文件内部的还是外部的 |
ContentTypes
ContentTypes 在zip压缩包的根目录下,文件名为 [Content_Types].xml ,它记录了该OPC文件中除了他自己以外的所有文件的类型。下面是一个PPTX文件的 ContentTypes 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<Types xmlns="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/package/2006/content-types">
<Default Extension="jpeg" ContentType="image/jpeg"/>
<Default Extension="rels" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-package.relationships+xml"/>
<Default Extension="xml" ContentType="application/xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/presentation.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation.main+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/slideMasters/slideMaster1.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slideMaster+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/slides/slide1.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slide+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/slides/slide2.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slide+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/presProps.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presProps+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/viewProps.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.viewProps+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/theme/theme1.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.theme+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/tableStyles.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.tableStyles+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/slideLayouts/slideLayout1.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slideLayout+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/ppt/slideLayouts/slideLayout2.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slideLayout+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/docProps/core.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-package.core-properties+xml"/>
<Override PartName="/docProps/app.xml" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.extended-properties+xml"/>
</Types>
其中有两种标签 Default 和 Override , Default 指明了拥有文件后缀名和文件类型的对应关系, Override 指明了某一个文件的文件类型。
比如:<Default Extension="jpeg" ContentType="image/jpeg"/> 的意思是后缀为 jpeg 的文件都是 image/jpeg 类型的文件,因此在OPC中不建议根据文件后缀名来判断一个文件的类型,而应该根据 ContentTypes 文件中记录的信息来判断文件类型。
*ML (* Markup Language)
关于各种
ML语言的详细信息请参考ECMA-376,Fifth Edition,Part 1。
Markup Language (ML) 译为 标记语言,是一种用 XML 来描述数据的"语言",比如:
| *ML | 全名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
PML |
Presentation Markup Language |
PPT 中各种数据的描述 |
WML |
Wordprocessing Markup Language |
Word 中数据的描述 |
SML |
Spreadsheet Markup Language |
Excel 中数据的描述 |
DML |
Drawing Markup Language |
Office 所有格式中都可以使用,用来描述矢量图形,图表等 |
SharedML |
Shared Markup Language |
描述了文档属性,音视频,图片,文档主题等内容,它被所有Office文件使用 |
比如之前提到的 presentation.xml 文件,它的文件内容就是在 PML 中定义的。具体信息可以查看 ECMA-376,Fifth Edition,Part 1。但是,ECMA-376 太长了,还没看就头疼,怎么办。
首先了解一下在 EMCA-376 中用来定义各种 ML 语言的 XSD:
XSD - XML Schema Definition 或者 XML Schema
XSD 类似 DTD,它们有相似的作用。在 ECMA-376 中,所有的 Markup Language 都是 XML 格式的,而这些 XML 的具体节点内容,都是用 XSD 来定义的,所以我们要对它有一定的了解:
XML Schema(XSD) 的作用:
- 定义可出现在文档中的元素
- 定义可出现在文档中的属性
- 定义哪个元素是子元素
- 定义子元素的次序
- 定义子元素的数目
- 定义元素是否为空,或者是否可包含文本
- 定义元素和属性的数据类型
- 定义元素和属性的默认值以及固定值
(可以在 这里 找到XSD的详细内容。)
在 XSD 中,有两个比较重要的概念:Simple Type(简单类型) 和 Complex Type(复杂类型):
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Simple Type Element | 简单类型元素,指那些仅包含文本的元素。它不会包含任何其他的元素或属性。 比如:<id>123</id>,这里元素 id 就是简单类型元素。 |
| Complex Type Element | 复杂类型元素,指那些可以包含其他任意元素或者属性的元素。 |
比如在 PML 中定义 页面大小(SlideSize) 这个元素(节点)的 XSD 如下:
<xsd:complexType name="CT_SlideSize">
<xsd:attribute name="cx" type="ST_SlideSizeCoordinate" use="required"/>
<xsd:attribute name="cy" type="ST_SlideSizeCoordinate" use="required"/>
<xsd:attribute name="type" type="ST_SlideSizeType" use="optional" default="custom"/>
</xsd:complexType>
可以看出 CT_SlideSize 是个 complexType(复杂类型) 的元素,并且它有三个 attribute(属性) ,分别是 cx , cy 和 type,根据它们 type 的前缀 ST_ ,可以看出这三个属性都是简单类型的,并且是 required 的。如果你明白了这里的描述,再去看 ECMA-376 中各种 ML 语言的定义应该会简单一点。
PS: 在看 ECMA-376 的时候可以先只看前 16 章的内容,只有160页左右,如果只算内容的话更少,后面的将近 5000 页都可以解析哪部分就去看哪部分就行了。言外之意就是,其实也没有想象中的那么唬人。JUST DO IT !
PPTX 解析的基本流程
这里以 PPTX 的解析为例,其它的 WORD 或者 EXCEL 可以触类旁通。
基本流程如下:
- 读取
/[Content_Types].xml文件,获取到所有文件的类型;
这部分需要了解 OPC 中关于 ContentTypes 的内容。 - 读取
/_rels/.rels这个所谓的Package Relationship文件,获取presentation.xml文件的位置,比如/ppt/presentation.xml;
这部分需要了解 OPC 中关于 Relationship 的内容以及 PML 的基本内容。 - 读取
/ppt/presentation.xml文件以及其关联的 Relationship 文件/ppt/_rels/presentation.xml.rels,得到该PPT所有页面文件的存储位置,比如/ppt/slides/slide1.xml,以及 slideMaster(母版)文件的存储位置,比如/ppt/slideMasters/slideMaster1.xml,以及 slideLayout(板式)等相关文件的存储位置;
这部分需要了解 PML 中关于 Presentation 的定义,也就是 PML 的 XSD 中定义的CT_Presentation类型。这个时候可以去详细的阅读 Presentation 章节的详细信息了。 - 读取
/ppt/slides/slide1.xml文件内容以及其关联的 Relationship/ppt/slides/_rels/slide1.xml.rels,可以得到该页面的所有元素信息;
这部分要完整解析就需要了解所有 PML、DML、SharedML 中的内容了。
不知道看到这里你还要不要自己解析啊?如果不愿意了,那大名鼎鼎的 POI 也许可以救你于水深火热。
POI/NPOI
POI 是 Apache 的项目,这里 是它的官网(NPOI 是 POI 的 .NET 版本)。背景知识我就不介绍了,这里摘自维基百科对它模块划分的介绍,可以在自己解析的时候参考:
POIFS (Poor Obfuscation Implementation File System) – This component reads and writes Microsoft's OLE 2 Compound document format. Since all Microsoft Office files are OLE 2 files, this component is the basic building block of all the other POI elements. POIFS can therefore be used to read a wider variety of files, beyond those whose explicit decoders are already written in POI.(也就是OPC模块)
HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Microsoft Excel (XLS) format files. It can read files written by Excel 97 onwards; this file format is known as the BIFF 8 format. As the Excel file format is complex and contains a number of tricky characteristics, some of the more advanced features cannot be read.()
XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Office Open XML (XLSX) format files. Similar feature set to HSSF, but for Office Open XML files.
HPSF (Horrible Property Set Format) – reads "Document Summary" information from Microsoft Office files. This is essentially the information that one can see by using the File|Properties menu item within an Office application.
HWPF (Horrible Word Processor Format) – aims to read and write Microsoft Word 97 (DOC) format files. This component is in initial stages of development.
XWPF (XML Word Processor Format) – similar feature set to HWPF, but for Office Open XML files.
HSLF (Horrible Slide Layout Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft PowerPoint files. This provides the ability to read, create and edit presentations (though some things are easier to do than others)
HDGF (Horrible DiaGram Format) – an initial pure Java implementation for Microsoft Visio binary files. It provides an ability to read the low level contents of the files.
HPBF (Horrible PuBlisher Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Publisher files.
HSMF (Horrible Stupid Mail Format[7][better source needed]) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Outlook MSG files.[8]
DDF (Dreadful Drawing Format) – a package for decoding the Microsoft Office Drawing format.
需要注意的是 POI 貌似对 PPT 的支持比较弱?
最后
完全解析 Office 格式是一项巨大的工程,开始之前要有充分的成本考虑。